Selecting the Right Aftercooler for Your Compressor System
Aftercoolers are essential for cooling compressed air, removing moisture, and protecting downstream equipment in industries like manufacturing, construction, and food processing. Selecting the appropriate aftercooler requires careful consideration of factors such as compressor size, operating conditions, and application needs to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Air-Cooled Aftercoolers: These use ambient air and fans for cooling, ideal for environments without water access, offering simplicity and low maintenance.
- Water-Cooled Aftercoolers: Utilize water for superior cooling efficiency, suited for high-pressure or high-temperature systems, but require water supply and treatment.
- Flow Rate Matching: Ensure the aftercooler’s capacity (SCFM) matches your compressor’s output to avoid inefficiencies or pressure drops.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider ambient temperature and dust levels, as these impact air-cooled aftercooler performance and maintenance needs.
- Application Requirements: Sensitive processes like food processing or spray painting require low dew points, often needing additional drying systems.
- Installation Space: Compact designs are crucial for mobile or space-constrained setups, while larger units suit stationary industrial systems.
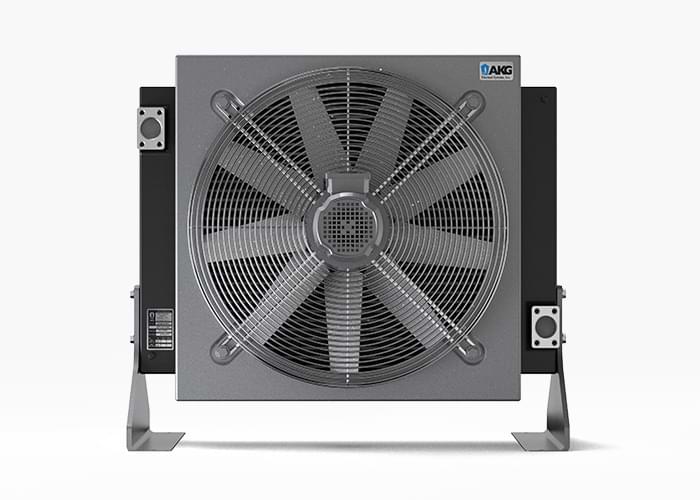
Air-Cooled Aftercoolers:
Compressor Applications
- Low Maintenance Designs
- AC or DC Power Options
- Flow Rates: 50-5,000 SCFM

Water-Cooled Aftercoolers:
Compressor Applications
- High-Efficiency Cooling
- Ideal for High-Pressure Systems
- Customizable Configurations
Guide to Selecting an Aftercooler
Aftercoolers are vital for cooling compressed air, removing up to 75% of moisture, and ensuring the reliability of compressor systems in applications ranging from industrial manufacturing to mobile construction. To select the right aftercooler, consider compressor output, environmental conditions, application requirements, and installation constraints. Air-cooled models are ideal for simplicity, while water-cooled units excel in high-heat environments. Proper sizing and material selection enhance efficiency and durability.
Key Selection Factors
Start by matching the aftercooler’s flow rate (SCFM) to your compressor’s output to avoid bottlenecks or excessive pressure drops. Evaluate ambient conditions—hot or dusty environments may require air-cooled units with robust fin designs or frequent maintenance. For applications like food processing or painting, pair the aftercooler with dryers to achieve low dew points. Consider space and power availability: compact, DC-powered units suit mobile setups, while AC-powered models are better for stationary systems. Materials like aluminum or stainless steel ensure corrosion resistance in harsh conditions.
Types of Aftercoolers
Air-cooled aftercoolers use fans to dissipate heat, offering low maintenance and no water requirements, ideal for construction or automotive applications. Water-cooled aftercoolers provide superior cooling for high-pressure systems but need a water source and treatment. Core-only units allow integration with existing airflow systems, while pneumatic-driven models are suited for hazardous environments. Each type can be customized with NPT or flange connections and anti-vibration mounts.


